Cricket
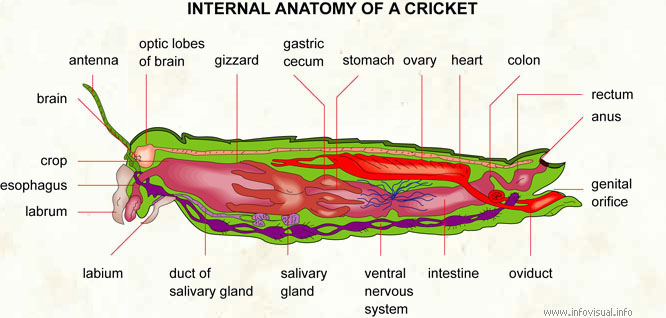
Antenna: organ of touch of a cricket.
Optic lobes of brain: portions of the brain that analyse visual stimuli.
Gizzard: part of the digestive tract that follows the crop.
Gastric cecum: cul-de-sac related to the stomach.
Stomach: penultimate portion of the digestive tract.
Ovary: egg-producing reproductive organ of a cricket.
Heart: blood-pumping organ.
Colon: intestine.
Rectum: last part of the digestive tract.
Anus: exit of the digestive tract.
Genital orifice: opening related to the reproductive organs.
Oviduct: passage that carries the eggs.
Intestine: final part of the digestive tract.
Ventral nervous system: collection of nerves in the abdomen of a cricket.
Salivary gland: saliva-producing glandular organ.
Duct of salivary gland: tube that carries the saliva.
Labium: lower lip of a cricket.
Labrum: upper lip of a cricket.
Esophagus: first part of the digestive tract.
Crop: bulge of the digestive tract.
Brain: seat of the mental faculties of a cricket.
Photo :
EN : Grasshoppers
FR : Sauterelles
ES : Saltamontes
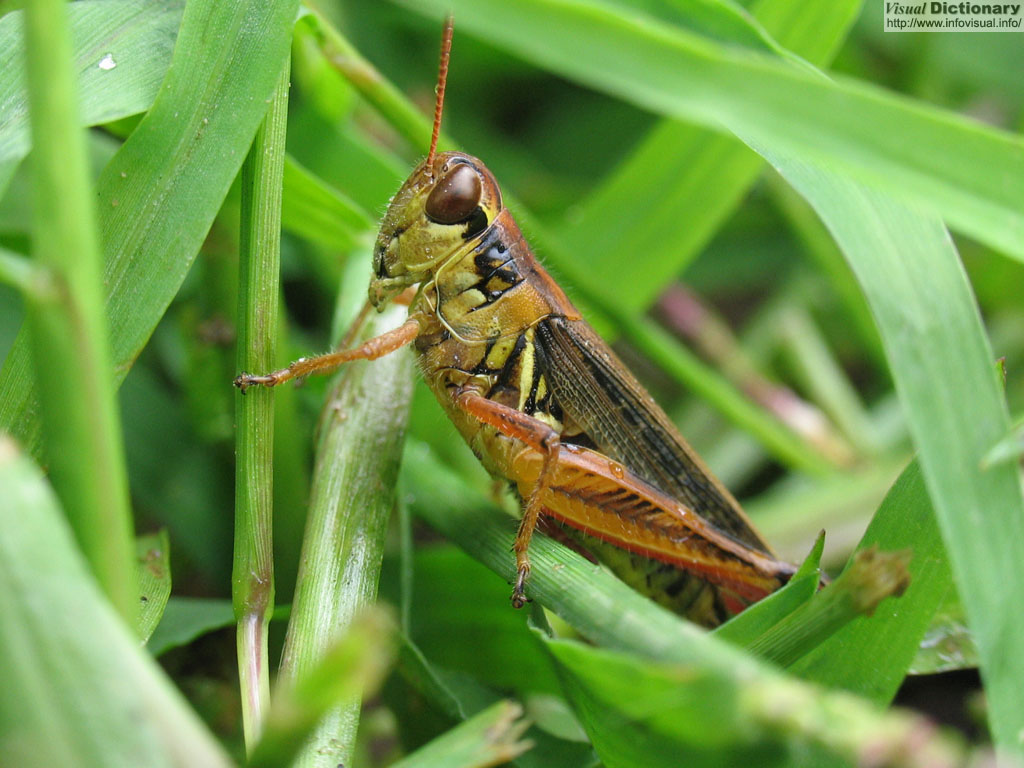

Grasshoppers are herbivorous insects of the suborder Caelifera in the order Orthoptera. To distinguish them from bush crickets or katydids, they are sometimes referred to as short-horned grasshoppers. Species that change colour and behaviour at high population densities are called locusts.
Animation : Cricket singing
Thanks to YouTube for allowing us to watch this video.