Finger
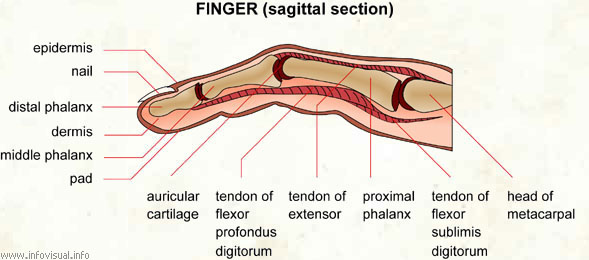
Head of metacarpal: top of the metacarpal bone.
Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis: tissue that connects the flexor sublimus digitorum to the phalange.
Proximal phalanx: first phalange.
Tendon of extensor: tissue that connects the extensor to the phalange.
Tendon of flexor digitorum profundus: tissue that connects the flexor profundus digitorum to the phalange.
Articular cartilage: elastic substance that allows flexibility of the joints between the phalanges.
Pad: fleshy part at the end of a finger.
Middle phalanx: second phalange.
Dermis: tissue forming the central layer of the skin.
Distal phalanx: third phalange.
Nail: horny plate on the dorsal surface of the end of a finger.
Epidermis: tissue forming the outer layer of the skin.
Photo :
EN : Hand
FR : main
ES : Mano

Like other paired organs (eyes, ears, legs), each hand is dominantly controlled by the opposing brain hemisphere, and thus handedness, or preferred hand choice for single-handed activities such as writing with a pen, reflects a significant individual trait.