Homme adulte (vue postérieure)
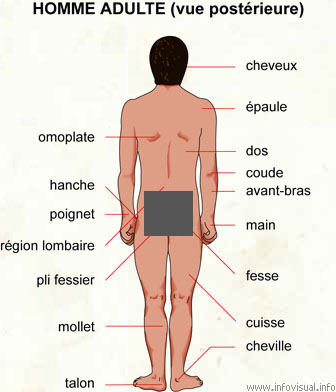
Cheveux: Poils situés sur le crâne, chez l'être humain.
Épaule: Articulation rejoignant le bras au tronc.
Dos: Partie postérieure du corps comprise entre les reins et la nuque.
Coude: Articulation reliant le bras à l'avant-bras.
Avant-bras: Partie du membre supérieur comprise entre le poignet et le coude.
Main: Partie du corps humain terminant le bras, composée de cinq doigts et servant au toucher et à la préhension.
Fesse: Chacune des deux parties de chair à la base du dos.
Cuisse: Haut du membre inférieur de l'homme contenant le fémur.
Cheville: Articulation rejoignant la jambe au pied.
Talon: Partie postérieure du pied.
Mollet: Surface musculaire, en arrière de la jambe, sous le genou.
Pli fessier: Rabat entre les deux fesses.
Région lombaire: Région du bas du dos, des reins.
Poignet: Articulation joignant l'avant-bras et la main.
Hanche: Partie du corps située entre la taille et le haut de la cuisse, sur le côté du corps.
Omoplate: Os triangulaire, plat et pair, situé dans le haut du dos.
Photo :

Domestic goats are one of the oldest domesticated species. For thousands of years, goats have been used for their milk, meat, hair, and skins all over the world. Most goats naturally have two horns, of various shapes and sizes depending on the breed. While horns are a predominantly male feature, some breeds of goats have horned females. Polled (hornless goats) are not uncommon and there have been incidents of polycerate goats (having as many as eight horns), although this is a genetic rarity thought to be inherited. Their horns are made of living bone surrounded by keratin and other proteins and are used for defense, dominance, and territoriality.
Goats are ruminants. They have a four-chambered stomach consisting of the rumen, the reticulum, the omasum, and the abomasum. Goats have horizontal slit-shaped pupils, an adaptation which increases peripheral depth perception. Because goats' irises are usually pale, the pupils are much more visible than in animals with horizontal pupils but very dark irises, such as sheep, cattle and most horses.
Both male and female goats have beards, and many types of goats may have wattles, one dangling from each side of the neck. Some breeds of sheep and goats appear superficially similar, but goat tails are short and point up, whereas sheep tails hang down and are usually longer, though some are short, and some long ones are docked.