Adult male (anterior view)
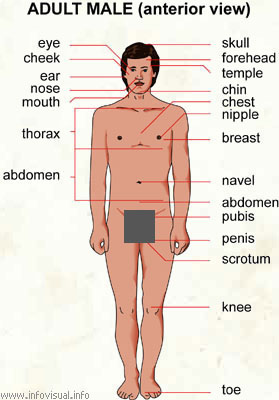
Skull: bony case of the brain.
Forehead: part of the face between the hairline and the eyebrows.
Temple: part of the head between the eye and the top of the ear.
Chin: protuberance of the jaw below the lower lip.
Chest: part of the upper trunk above the diaphragm and over the ribs.
Nipple: conical protuberance forming the point of the breast.
Breast: part of the human chest which contains the mammary gland.
Navel: mark left by the umbilical cord.
Abdomen: lower part of the trunk, containing the digestive organs.
Pubis: area at the base of the lower abdomen covered by pubic hairs.
Penis: external reproductive organ of a human male.
Scrotum: small sac under the human penis containing the testicles.
Knee: joint between the thigh and the lower leg.
Toe: digit of the foot.
Abdomen: lower part of the trunk, containing the digestive organs.
Thorax: the part of the upper trunk above the diaphragm and over the ribs.
Mouth: entrance to the digestive tract, situated in the lower part of the face.
Nose: projecting part of the face between the mouth and the forehead, site of respiration.
Ear: external organ of hearing.
Cheek: part of the face between the nose and the ear, and the eye and the lower jaw.
Eye: sight organ.
Photo :

Domestic goats are one of the oldest domesticated species. For thousands of years, goats have been used for their milk, meat, hair, and skins all over the world. Most goats naturally have two horns, of various shapes and sizes depending on the breed. While horns are a predominantly male feature, some breeds of goats have horned females. Polled (hornless goats) are not uncommon and there have been incidents of polycerate goats (having as many as eight horns), although this is a genetic rarity thought to be inherited. Their horns are made of living bone surrounded by keratin and other proteins and are used for defense, dominance, and territoriality.
Goats are ruminants. They have a four-chambered stomach consisting of the rumen, the reticulum, the omasum, and the abomasum. Goats have horizontal slit-shaped pupils, an adaptation which increases peripheral depth perception. Because goats' irises are usually pale, the pupils are much more visible than in animals with horizontal pupils but very dark irises, such as sheep, cattle and most horses.
Both male and female goats have beards, and many types of goats may have wattles, one dangling from each side of the neck. Some breeds of sheep and goats appear superficially similar, but goat tails are short and point up, whereas sheep tails hang down and are usually longer, though some are short, and some long ones are docked.