External ear
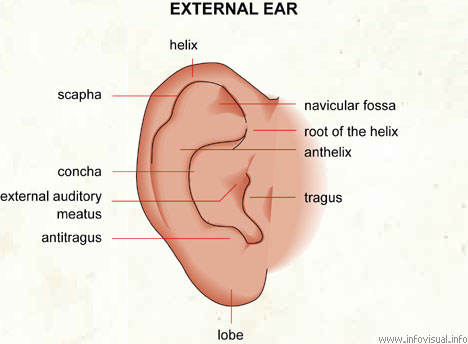
Helix: fold surrounding the auricle.
Navicular fossa: boat-shaped fold of the ear.
Root of the helix: part of the helix.
Anthelix: curved ridge in front of the helix.
Tragus: prominence over and in front of the acoustic meatus.
Lobe: fleshy part at the base of the ear.
Antitragus: ear projection opposite the tragus.
External auditory meatus: mouth of the canal of the temporal bone that carries sounds to the eardrum.
Concha: deep fossa of the external ear.
Scapha: hollow at the end of the helix.
Photo :
EN : Human
ear
FR : L'oreille
humaine
ES : Oído
humano
The ear is the sense organ that detects sounds. The vertebrate ear shows a common biology from fish to humans, with variations in structure according to order and species. It not only acts as a receiver for sound, but plays a major role in the sense of balance and body position.