Classical guitar
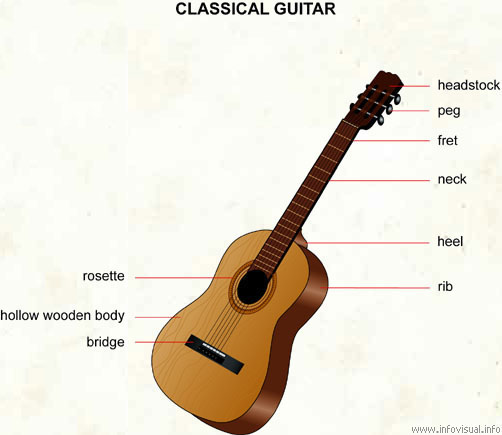
Headstock: part at the top of the neck where the pegs are located.
Peg: small button used to control the tension of the strings.
Fret: metal piece that marks the position of the notes.
Neck: part of the guitar where strings are pressed to produce the notes.
Heel: piece that fasten the neck to the body of the guitar.
Rib: piece of wood between the body and the bottom.
Bridge: piece that supports the strings and transmits the vibrations to the body.
Hollow wooden body: hollow part that amplifies the sounds.
Rosette: wooden pattern around the soundhole.
Photo :
EN : Bells
(ceramic)
FR : Cloche
ES : Campana

A bell is a simple sound-making device. The bell is a percussion instrument and an idiophone. Its form is usually an open-ended hollow drum which resonates upon being struck. The striking implement can be a tongue suspended within the bell, known as a clapper, a small, free sphere enclosed within the body of the bell, or a separate mallet. Bells are usually made of cast metal, but small bells can also be made from ceramic or glass. Bells can be of all sizes: from tiny dress accessories to church bells weighing many tons.