Bones of the hand
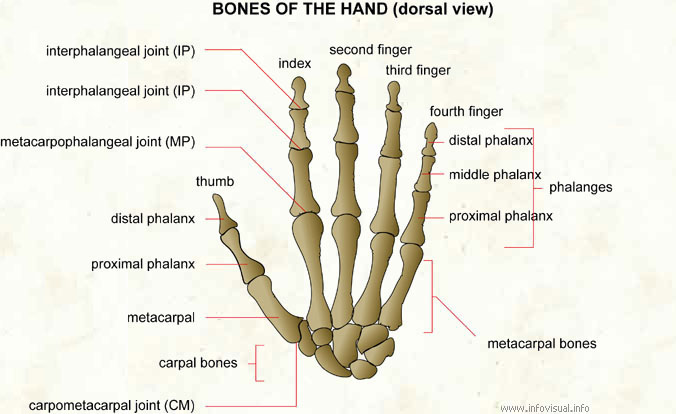
Index: second finger of the hand, next to the thumb.
Second finger: middle finger of the hand.
Third finger: second finger from the outside of the hand.
Fourth finger: small finger closest to the outside of the hand.
Distal phalanx: bone at the end of a finger.
Middle phalanx: small, middle bone of a finger.
Proximal phalanx: small bone of a finger, closest to the palm of the hand.
Phalanges: jointed segment of a finger.
Metacarpal bones: bones of the hand between the carpals and the phalanges.
Carpometacarpal joint (CM): joint of the carpus and metacarpus.
Carpal bones: jointed parts of the hand between the forearm and the metacarpals.
Thumb: the largest, shortest and most important of the digits of the hand.
Metacarpophalangeal joint (MP): joint between the metacarpals and the phalanges.
Interphalangeal joint (IP): joint between the first and second phalanges.
Interphalangeal joint (IP): joint between the second and third phalanges.
Photo :
EN : Hand
FR : main
ES : Mano

Like other paired organs (eyes, ears, legs), each hand is dominantly controlled by the opposing brain hemisphere, and thus handedness, or preferred hand choice for single-handed activities such as writing with a pen, reflects a significant individual trait.
Animation : Hand
Thanks to YouTube for allowing us to watch this video.