Anatomia interna de un pez óseo
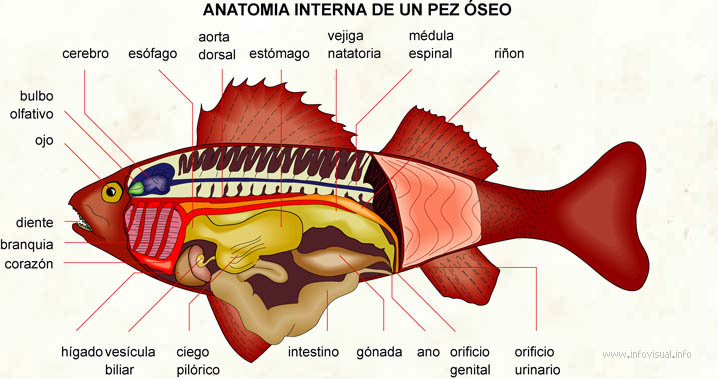
Cerebro: parte donde están las capacidades mentales del pez.
Esófago: parte del tubo digestivo situado entre la boca y el estómago.
Aorta dorsal: vaso sanguineo dorsal que transporta la sangre del corazón a los órganos.
Estómago: órgano del tubo digestivo situado entre el esófago y el intestino.
Vejiga natatoria: depósito en la que almacena la orina.
Médula espinal: parte del sistema nervioso que une el cerebro a todas las partes del pez.
Riñon: órgano de purificación sanguinea.
Orificio urinario: apertura relativo a la orina.
Orificio genital: apertura relativo a los órganos genitales.
Ano: orificio del tubo digestivo.
Gónada: glándula sexual del pez.
Intestino: última parte del tubo digestivo.
Ciego pilórico: conducto relativo al intestino.
Vesícula biliar: saco pequeño que contiene la bilis.
Hígado: glándula digestiva que hace la bilis.
Corazón: órgano de la circulación sanguínea.
Branquia: órgano respiratorio del pez.
Diente: órgano duro del pez que sirve a masticar los alimentos.
Ojo: órgano de la vista del pez.
Bulbo olfativo: parte abultada del órgano de la percepción de los olores.
Foto :
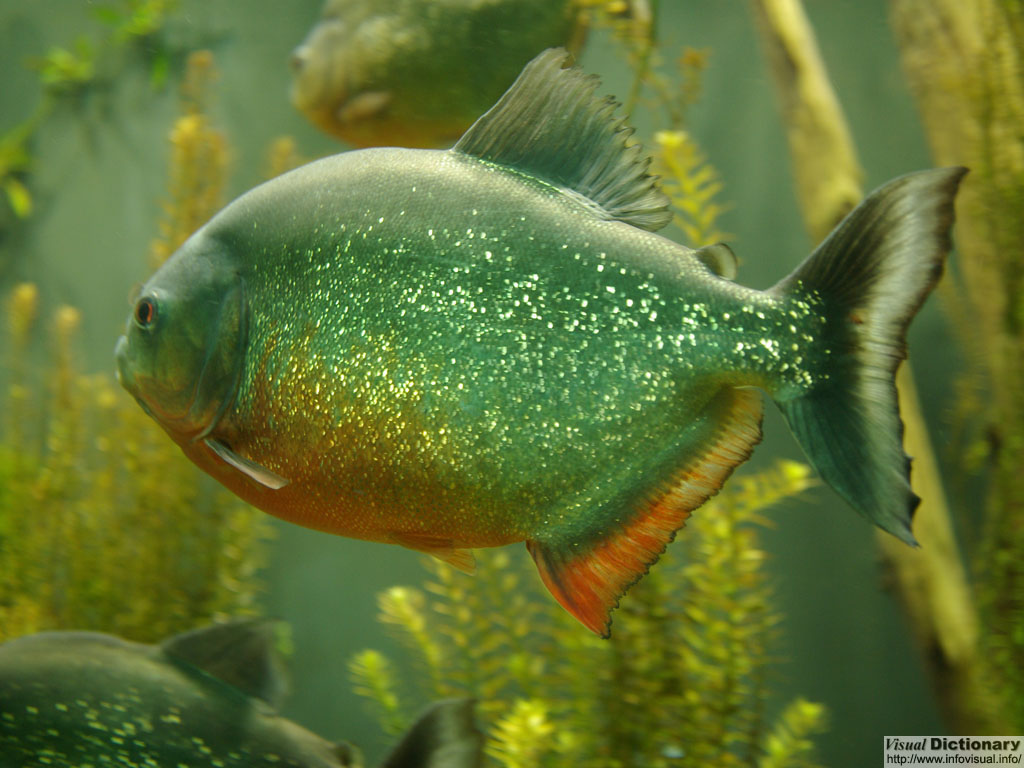

A Piranha or piraña is a member of a family of omnivorous freshwater fish which live in South American rivers. In Venezuelan rivers they are called caribes. They are known for their sharp teeth and an aggressive appetite for meat. Piranhas are not generally violent and have been known to be domesticated in home and office fish tanks. Piranhas belong to the family of Serrasalmidae. Traditionally, only the four genera Pristobrycon, Pygocentrus, Pygopristis, and Serrasalmus are considered to be true piranhas, due to their specialized teeth. However, a recent analysis showed that, if the piranha group is to be monophyletic, it should be restricted to Serrasalmus, Pygocentrus, and part of Pristobrycon, or expanded to include these taxa plus Pygopristis, Catoprion, and Pristobrycon striolatus. Pygopristis was found to be more closely related to Catoprion than the other three piranha genera.
Piranhas are found only in the Amazon basin, in the Orinoco, in rivers of the Guyanas, in the Paraguay-Paraná, and in the São Francisco River systems; some species of piranha have extremely broad geographic ranges, occurring in more than one of the major basins mentioned above, whereas others appear to have much more limited distributions. However, piranha have been introduced into parts of the United States, even being occasionally found in the Potomac River, but they typically do not survive the cold winters of that region. Recently a piranha was caught by a fisherman in the Catawba River in North Carolina. This is the first known case in North Carolina and possibly in the region. Piranha have also been discovered in the Kaptai Lake in South-East Bangladesh. Research is being carried out to establish how piranha have moved to such distant corners of the world from their original habitat. It is anticipated that rogue exotic fish traders have released them in the lake to avoid being caught by anti-poaching forces.