Animales acuaticos
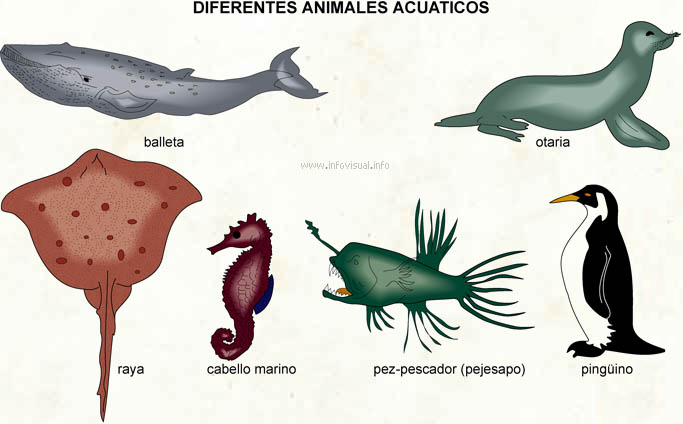
Balleta: mamífero marino se alimenta de plancton.
Otaria: mamífero acuatico se alimenta de peces y puede moverse en la tierra con sus miembros anteriores.
Raya: pez cartilaginoso que vive cerca de los fondos marinos.
Cabello marino: animal marino perteneciente a la categoría de los peces, que se tiene en posición vertical.
Pez-pescador (pejesapo): pez de las partes muy profundas de la mar.
Pinguino: ave del océano árctico a los pies palmados, se alimenta de peces.
Foto :
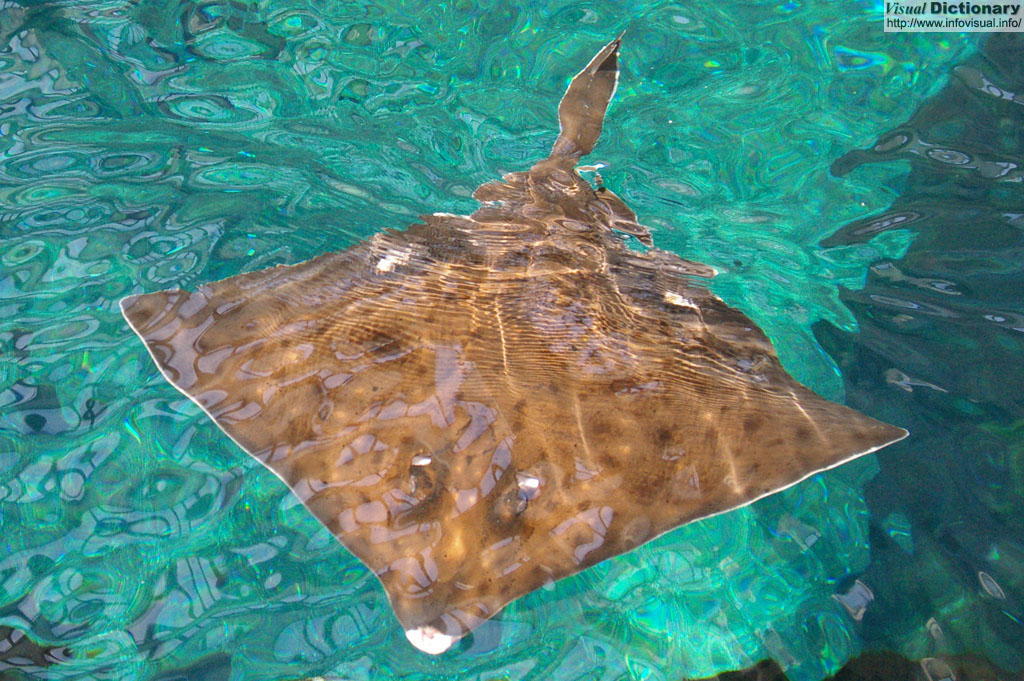

Batoidea is a superorder of cartilaginous fishes containing more than 500 described species in thirteen families. They are commonly known as rays, but that term is also used specifically for batoids in the order Rajiformes, the "true ray". Batoids include stingrays, skates, electric rays, guitarfishes and sawfishes.
Batoids are flat-bodied, and, like sharks, are a species of cartilaginous marine fish, meaning they have a boneless skeleton made of a tough, elastic substance. Batoids also are like sharks in having slot-like body openings called gill slits that lead from the gills. Batoid gill slits lie under the pectoral fins on the underside, whereas a shark's are on the sides of the head. Most batoids have a flat, disk-like body, with the exception of the guitarfishes and sawfishes, while most sharks have a streamlined body. Many species of batoid have developed their pectoral fins into broad flat wing-like appendages. The eyes and spiracles are located on top of the head.
Animation : Subacuático
Gracias a YouTube de permitirnos d'observar este vídeo.